
Option C - Energy
Question 1
SLPaper 3Nuclear fission of 235U is one source of electrical energy that has a minimal carbonfootprint.
Natural uranium needs to be enriched to increase the proportion of 235U. Suggesta technique that would determine the relative abundances of 235U and 238U.
Explain how 235U fission results in a chain reaction, including the concept ofcritical mass.
Suggest one reason why there is opposition to the increased use of nuclear fissionreactors.
Question 2
SLPaper 3This question is about global warming.
State one greenhouse gas, other than carbon dioxide.
Describe the effect of infrared (IR) radiation on carbon dioxide molecules.
Outline one approach to controlling industrial emissions of carbon dioxide.
Question 3
SLPaper 3Octane number is a measure of the performance of engine fuel.
Suggest why a high-octane number fuel is preferable.
Reforming reactions are used to increase the octane number of a hydrocarbon fuel.
Suggest the structural formulas of two possible products of the reforming reaction of heptane, C7H16.
b(i).
The 1H NMR spectrum of one of the products has four signals. The integration trace shows a ratio of the areas under the signals of 9 : 3 : 2 : 2.
Deduce the structural formula of the product.
b(ii).
Question 4
HLPaper 3Photovoltaic cells are much less hazardous than nuclear fission.
Early photovoltaic cells were based on silicon containing traces of other elements.State the type of semiconductor produced by doping silicon with indium, In, giving areason that refers to its electronic structure.
Dye-sensitized solar cells, DSSCs, use a dye to absorb the sunlight. State twoadvantages that DSSCs have over traditional silicon based photovoltaic cells.
The structure of two dyes used in DSSCs are shown.
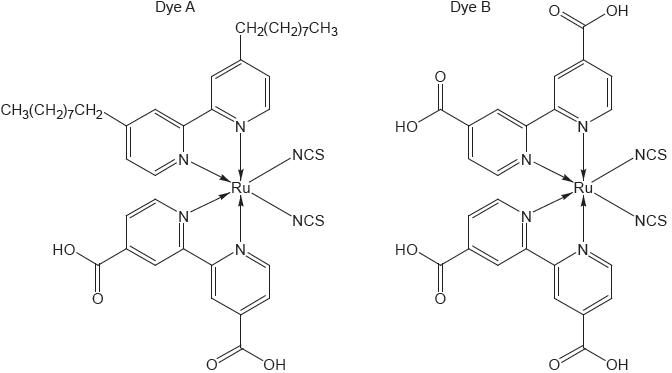
Predict, giving a reason, which dye will absorb light of longer wavelength.
Question 5
SLPaper 3Carbon dioxide and water vapour are greenhouse gases produced by the combustion of fossil fuels.
Explain the effect of the increasing concentration of atmospheric carbon dioxide on the acidity of oceans.
(i) Describe the changes that occur at the molecular level when atmospheric carbon dioxide gas absorbs infrared radiation emitted from the Earth’s surface.
(ii) Other than changes to the acidity of oceans, suggest why the production of carbon dioxide is of greater concern than the production of water vapour.
Question 6
SLPaper 3Nuclear power is another source of energy.
Compare and contrast the process of nuclear fusion with nuclear fission.

Dubnium-261 has a half-life of 27 seconds and rutherfordium-261 has a half-life of81 seconds.
Estimate what fraction of the dubnium-261 isotope remains in the same amount of timethat 3 4 of rutherfordium-261 decays.
Question 7
SLPaper 3The process of converting heat to electricity is limited by its thermal (Carnot) efficiency.
Thermal efficiency = temp. of steam at source (K) − temp. heat sink (K) temp. of steam at source (K) × 100
Calculate the thermal efficiency of a steam turbine supplied with steam at 540°C andusing a river as the choice of sink at 23 °C.
Power plants generating electricity by burning coal to boil water operate atapproximately 35% efficiency.
State what this means and suggest why it is lower than the thermal efficiency.
Question 8
SLPaper 3This question is about fuel for engines.
Crude oil can be converted into fuels by fractional distillation and cracking.
Contrast these two processes.

Determine the specific energy, in kJ g−1, and energy density, in kJ cm−3, of hexane, C6H14. Give both answers to three significant figures.
Hexane: Mr = 86.2; ΔHc = −4163 kJ mol−1; density = 0.660 g cm−3
Specific energy:
Energy density:
Hydrocarbons need treatment to increase their octane number to prevent pre-ignition (knocking) before they can be used in internal combustion engines.
Describe how this is carried out and the molecular changes that take place.
Question 9
SLPaper 3There are many sources of energy available.
State one advantage and one disadvantage for each energy source in the table.

Calculate the specific energy of hydrogen, stating its units. Refer to sections 1,6 and 13 of the data booklet.
Hydrogen has a higher specific energy than petrol (gasoline) but is not used as aprimary fuel source in cars. Discuss the disadvantages of using hydrogen.
Question 10
SLPaper 3In the 20th Century, both fission and fusion were considered as sources of energy but fusion waseconomically and technically unattainable.
Compare and contrast fission and fusion in terms of binding energy and the typesof nuclei involved.
Suggest two advantages that fusion has over fission.
The amount of 228Ac in a sample decreases to one eighth ( 1 8 ) of its original value inabout 18 hours due to β-decay. Estimate the half-life of 228Ac.
