
Option A - Materials
Question 1
SLPaper 3Infrared (IR) spectroscopy is often used for the identification of polymers, such as PETE, forrecycling.
LDPE and high density polyethene (HDPE) have very similar IR spectra even thoughthey have rather different structures and physical properties.
Below are the IR spectra of two plastics (A and B); one is PETE, the other is lowdensity polyethene (LDPE).

Deduce, giving your reasons, the identity and resin identification code (RIC) of A and Busing sections 26 and 30 of the data booklet.

Describe the difference in their structures.
Explain why the difference in their structures affects their melting points.
Question 2
SLPaper 3Chemical vapour deposition (CVD) produces multi-walled carbon nanotubes (MWCNT) of amore appropriate size for use in liquid crystals than production by arc discharge.
State the source of carbon for MWCNT produced by arc discharge and by CVD.

Discuss three properties a substance should have to be suitable for use in liquidcrystal displays.
Question 3
HLPaper 3X-ray crystallography of a metal crystal produces a diffraction pattern of bright spots.

Using X-rays of wavelength 1.54 × 10−10 m, the first bright spots were produced at an angle θ of 22.3° from the centre.
Calculate the separation between planes of atoms in the lattice, in meters, using section 1 of the data booklet.
Question 4
HLPaper 3Antimony oxide is widely used as a homogeneous catalyst for the reaction ofbenzene-1,4-dicarboxylic acid with ethane-1,2-diol in the production of polyethyleneterephthalate (PETE).

Deduce the repeating unit of the polymer and the other product of the reaction.

State the class of polymer to which PETE belongs.
Question 5
SLPaper 3One way of classifying materials is based on the type of bonding present.
One reaction to convert cyclohexanone to caprolactam using concentrated sulfuric acidas a catalyst is shown.

Outline why this type of classification is not entirely satisfactory by using magnesiumdiboride, MgB2,as an example. Refer to sections 8 and 29 of the data booklet.
Structures of poly(methyl acrylate), PMA, and Bakelite® are shown.

Suggest, giving reasons, which is the thermoplastic polymer and which is thethermosetting polymer.

In an incomplete combustion of the polyvinyl chloride, PVC, it was found thathydrogen chloride, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and water vapour were released.

Formulate an equation for this reaction using the formula of the PVCrepeating unit.
A zeolite is an alternative catalyst for this reaction.
Explain how zeolites act as selective catalysts.
Identify another advantage of using a zeolite instead of concentrated sulfuric acid.
Repeating units of several polymers are listed.

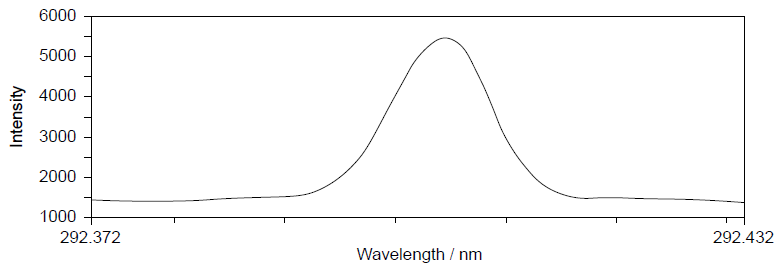
The infrared (IR) spectrum of one of these polymers is shown.

Deduce, giving a reason, the name of this polymer and its Resin Identification Code(RIC), using sections 26 and 30 in the data booklet.

Question 6
HLPaper 3One way of classifying materials is based on the type of bonding present.
Caprolactam reacts with water to form compound X, a monomer.

One way of classifying materials is based on the type of bonding present.
One reaction to convert cyclohexanone to caprolactam using concentrated sulfuric acidas a catalyst is shown.

Outline why this type of classification is not entirely satisfactory by using magnesiumdiboride, MgB2,as an example. Refer to sections 8 and 29 of the data booklet.
Structures of poly(methyl acrylate), PMA, and Bakelite® are shown.

Suggest, giving reasons, which is the thermoplastic polymer and which is thethermosetting polymer.

A zeolite is an alternative catalyst for this reaction.
Explain how zeolites act as selective catalysts.
State the names of the two terminal functional groups in X.
Deduce the repeating unit of the polymer of X.
Repeating units of several polymers are listed.

The infrared (IR) spectrum of one of these polymers is shown.

Deduce, giving a reason, the name of this polymer and its Resin Identification Code(RIC), using sections 26 and 30 in the data booklet.

Question 7
SLPaper 3Rhodium and palladium are often used together in catalytic converters. Rhodium is a goodreduction catalyst whereas palladium is a good oxidation catalyst.
In a catalytic converter, carbon monoxide is converted to carbon dioxide. Outline theprocess for this conversion referring to the metal used.
Nickel is also used as a catalyst. It is processed from an ore until nickel(II)chloride solution is obtained. Identify one metal, using sections 24 and 25 of thedata booklet, which will not react with water and can be used to extract nickelfrom the solution.
Deduce the redox equation for the reaction of nickel(II) chloride solution with themetal identified in (b)(i).
Another method of obtaining nickel is by electrolysis of a nickel(II) chloride solution.Calculate the mass of nickel, in g, obtained by passing a current of 2.50 A through thesolution for exactly 1 hour. Charge (Q) = current (I) × time (t).
Question 8
HLPaper 3Chromium forms coloured compounds and is used to make stainless and hard steel. The distance between layers of chromium atoms in the metal can be obtained using X-ray crystallography.
(i) The diagram below shows the diffraction of two X-ray beams, y and z of wavelength λ, shining on a chromium crystal whose planes are a distance d nm apart.

Deduce the extra distance travelled by the second beam, z, compared to the first one, y.
(ii) State the Bragg’s condition for the observed diffraction to be at its strongest (constructive interference).
(i) The mass of one unit cell of chromium metal is 17.28 × 10−23g. Calculate the number of unit cells in one mole of chromium. _A_r(Cr) = 52.00.
(ii) Deduce the number of atoms of chromium per unit cell.
Question 9
SLPaper 3Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP) used with Mass Spectrometry (MS) or Optical EmissionSpectrometry (OES) can be used to identify and quantify elements in a sample.
The following graphs represent data collected by ICP-OES on trace amounts ofvanadium in oil.
Graph 1: Calibration graph and signal for 10 μg kg−1 of vanadium in oil

Graph 2: Calibration of vanadium in μg kg−1

[Source: © Agilent Technologies, Inc.1998. Reproduced with Permission, Courtesy of Agilent Technologies, Inc.]
ICP-OES/MS can be used to analyse alloys and composites. Distinguish betweenalloys and composites.
ICP-MS is a reference mode for analysis. The following correlation graphs betweenICP-OES and ICP-MS were produced for yttrium and nickel.
Each y-axis shows concentrations calculated by ICP-OES; each x-axis shows concentrationsfor the same sample as found by ICP-MS.
The line in each graph is y = x.
Discuss the effectiveness of ICP-OES for yttrium and nickel.
Identify the purpose of each graph.

Calculate, to four significant figures, the concentration, in μg kg−1, of vanadium inoil giving a signal intensity of 14 950.
Vanadium(V) oxide is used as the catalyst in the conversion of sulfur dioxide tosulfur trioxide.
SO2(g) + V2O5(s) → SO3(g) + 2VO2(s)
1 2 O2(g) + 2VO2(s) → V2O5(s)
Outline how vanadium(V) oxide acts as a catalyst.
Question 10
SLPaper 3Research has led to the discovery of new catalysts that are in high demand and used in many chemical industries.
Explain, with reference to their structure, the great selectivity of zeolites as catalysts.
Nanocatalysts play an essential role in the manufacture of industrial chemicals.
(i) Describe the high pressure carbon monoxide (HIPCO) method for the production of carbon nanotubes.
(ii) Outline one benefit of using nanocatalysts compared to traditional catalysts in industry.
