
Topic 21 - Measurement & Analysis (HL)
Question 1
HLPaper 3X-ray crystallography of a metal crystal produces a diffraction pattern of bright spots.

Using X-rays of wavelength 1.54 × 10−10 m, the first bright spots were produced at an angle θ of 22.3° from the centre.
Calculate the separation between planes of atoms in the lattice, in meters, using section 1 of the data booklet.
Question 2
HLPaper 2A 4.406 g sample of a compound containing only C, H and O was burnt in excess oxygen.8.802 g of CO2 and 3.604 g of H2O were produced.
The following spectrums show the Infrared spectra of propan-1-ol, propanal and propanoic acid.

NIST Mass Spectrometry Data Center Collection © 2021 copyright by the U.S. Secretary of Commerce on behalf of__the United States of America. All rights reserved. Available at: https://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?ID=C71238&Units=SI&Type=IRSPEC&Index=3#IR-SPEC [Accessed 6 May 2020]. Source adapted.

NIST Mass Spectrometry Data Center Collection © 2021 copyright by the U.S. Secretary of Commerce on behalf of__the United States of America. Available at: https://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?ID=C79094&Units=SI&Mask=80#IR-Spec [Accessed 6 May 2020]. Source adapted.

NIST Mass Spectrometry Data Center Collection © 2021 copyright by the U.S. Secretary of Commerce on behalf of the United States of America. Available at: https://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?Name=propanal&Units=SI&cIR=on&cTZ=on#IRSpec [Accessed 6 May 2020]. Source adapted.
Determine the empirical formula of the compound using section 6 of the data booklet.
Determine the molecular formula of this compound if its molar mass is 88.12 g mol−1. If you did not obtain an answer in (a) use CS, but this is not the correct answer.
Identify each compound from the spectra given, use absorptions from the range of 1700 cm−1 to 3500 cm−1. Explain the reason for your choice, referring to section 26 of the data booklet.

Predict the number of 1H NMR signals, and splitting pattern of the –CH3 seen for propanone (CH3COCH3) and propanal (CH3CH2CHO).

Predict the fragment that is responsible for a m/z of 31 in the mass spectrum of propan‑1‑ol. Use section 28 of the data booklet.
Question 3
HLPaper 2Ethane-1,2-diol, HOCH2CH2OH, has a wide variety of uses including the removal of ice from aircraft and heat transfer in a solar cell.
(i) Calculate Δ_H_θ, in kJ, for this similar reaction below using Δ H f θ data from section 12 of the data booklet. Δ H f θ of HOCH2CH2OH(l) is –454.8kJmol-1.
2CO (g) + 3H2 (g) ⇌HOCH2CH2OH (l)
(ii) Deduce why the answers to (a)(iii) and (b)(i) differ.
(iii) Δ_S_θfor the reaction in (b)(i) is –620.1JK-1. Comment on the decrease in entropy.
(iv) Calculate the value of ΔGθ, in kJ, for this reaction at 298 K using your answer to (b)(i). (If you did not obtain an answer to (b)(i), use –244.0 kJ, but this is not the correct value.)
(v) Comment on the statement that the reaction becomes less spontaneous as temperature is increased.
Predict the 1HNMR data for ethanedioic acid and ethane-1,2-diol by completing the table.

Question 4
HLPaper 1Which would be the most effective method to distinguish between liquid propan-1-ol and propan-2-ol?
Question 5
HLPaper 2Urea, (H2N)2CO, is excreted by mammals and can be used as a fertilizer.
Urea can also be made by the direct combination of ammonia and carbon dioxide gases.
2NH3(g) + CO2(g) ⇌ (H2N)2CO(g) + H2O(g) Δ_H_ < 0
Calculate the percentage by mass of nitrogen in urea to two decimal places using section 6 of the data booklet.
Suggest how the percentage of nitrogen affects the cost of transport of fertilizers giving a reason.
The structural formula of urea is shown.
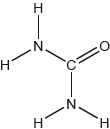
Predict the electron domain and molecular geometries at the nitrogen and carbon atoms, applying the VSEPR theory.
Urea can be made by reacting potassium cyanate, KNCO, with ammonium chloride, NH4Cl.
KNCO(aq) + NH4Cl(aq) → (H2N)2CO(aq) + KCl(aq)
Determine the maximum mass of urea that could be formed from 50.0 cm3 of 0.100 mol dm−3 potassium cyanate solution.
State the equilibrium constant expression, _K_c.
Predict, with a reason, the effect on the equilibrium constant, _K_c, when the temperature is increased.
Determine an approximate order of magnitude for _K_c, using sections 1 and 2 of the data booklet. Assume Δ_G_Θfor the forward reaction is approximately +50 kJ at 298 K.
Suggest one reason why urea is a solid and ammonia a gas at room temperature.
Sketch two different hydrogen bonding interactions between ammonia and water.
The combustion of urea produces water, carbon dioxide and nitrogen.
Formulate a balanced equation for the reaction.
Calculate the maximum volume of CO2, in cm3, produced at STP by the combustion of 0.600 g of urea, using sections 2 and 6 of the data booklet.
Describe the bond formation when urea acts as a ligand in a transition metal complex ion.
The C–N bonds in urea are shorter than might be expected for a single C–N bond. Suggest, in terms of electrons, how this could occur.
The mass spectrum of urea is shown below.
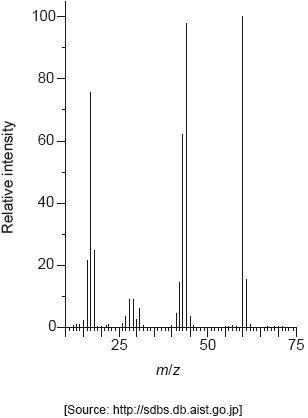
Identify the species responsible for the peaks at m/z = 60 and 44.

The IR spectrum of urea is shown below.
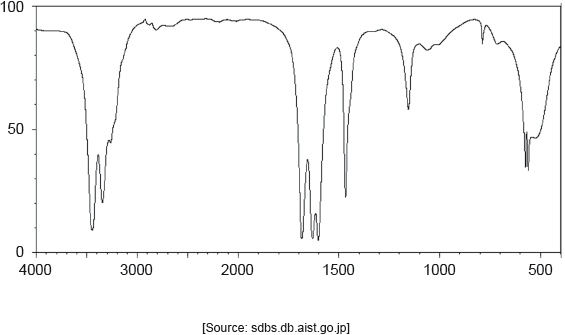
Identify the bonds causing the absorptions at 3450 cm−1 and 1700 cm−1 using section 26 of the data booklet.

Predict the number of signals in the 1H NMR spectrum of urea.
Predict the splitting pattern of the 1H NMR spectrum of urea.
Outline why TMS (tetramethylsilane) may be added to the sample to carry out 1H NMR spectroscopy and why it is particularly suited to this role.
Question 6
HLPaper 1Which compound with the molecular formula C4H8O has this high resolution H1 NMR?

From: libretexts.org. Courtesy of Chris Schaller, Professor (Chemistry)
at College of Saint Benedict/Saint John’sUniversity.
Question 7
HLPaper 2Nitric acid is usually produced by the oxidation of ammonia.
A mixture of nitric acid and sulfuric acid can be used to convert benzene to nitrobenzene, C6H5NO2.
Draw arrows in the boxes to represent the electron configuration of a nitrogen atom.

a(i).
Deduce a Lewis (electron dot) structure of the nitric acid molecule, HNO3, that obeys the octet rule, showing any non-zero formal charges on the atoms.
a(ii).
Explain the relative lengths of the three bonds between N and O in nitric acid.
a(iii).
State a technique used to determine the length of the bonds between N and O in solid HNO3.
a(iv).
Write an equation for the reaction between the acids to produce the electrophile, NO2+.
b(i).
Draw the structural formula of the carbocation intermediate produced when this electrophile attacks benzene.
b(ii).
Deduce the number of signals that you would expect in the 1H NMR spectrum of nitrobenzene and the relative areas of these.

b(iii).
Question 8
HLPaper 1What information can be deduced from the splitting pattern of 1H NMR signals?
Question 9
HLPaper 1Which can be identified using infrared (IR) spectroscopy?
Question 10
HLPaper 1Which technique can be used to identify bond length and bond angle?
