
Option D - Astrophysics
Question 1
HLPaper 3Describe how some white dwarf stars become type Ia supernovae.
Hence, explain why a type Ia supernova is used as a standard candle.
Explain how the observation of type Ia supernovae led to the hypothesis that dark energy exists.
Question 2
HLPaper 3Recent evidence from the Planck observatory suggests that the matter density of the universe is , where is the critical density.
The graph shows the variation with time t of the cosmic scale factor R in the flat model of the universe in which dark energy is ignored.
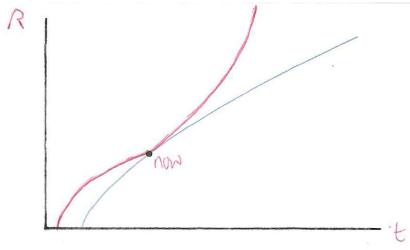
On the axes above draw a graph to show the variation of R with time, when dark energy is present.
The density of the observable matter in the universe is only 0.05 . Suggest how the remaining 0.27 is accounted for.
The density of dark energy is where . Calculate the amount of dark energy in 1 of space.
Question 3
SLPaper 3Outline how the light spectra of distant galaxies are used to confirm hypotheses about the expansion of the universe. a(i).
Light from a hydrogen source in a laboratory on Earth contains a spectral line of wavelength 122 nm. Light from the same spectral line reaching Earth from a distant galaxy has a wavelength of 392 nm. Determine the ratio of the present size of the universe to the size of the universe when the light was emitted by the galaxy.a(ii).
Estimate the age of the universe in seconds using the Hubble constant . b(i).
Outline why the estimate made in is unlikely to be the actual age of the universe. .
Question 4
HLPaper 3A distinctive feature of the constellation Orion is the Trapezium, an open cluster of stars within Orion.Mintaka is one of the stars in Orion.
Distinguish between a constellation and an open cluster.
The parallax angle of Mintaka measured from Earth is arc-second. Calculate, in parsec, the approximate distance of Mintaka from Earth.
State why there is a maximum distance that astronomers can measure using stellar parallax.
The Great Nebula is located in Orion. Describe, using the Jeans criterion, the necessary condition for a nebula to form a star.
Question 5
HLPaper 3A galaxy can be modelled as a sphere of radius . The distance of a star from the centre of the galaxy is .
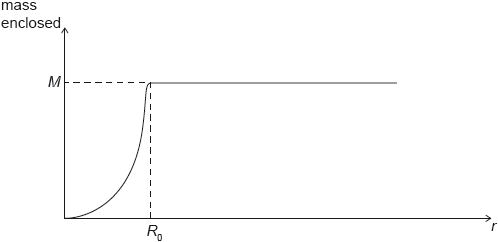 For this model the graph is a simplified representation of the variation with of the mass of visible matter enclosed inside .
For this model the graph is a simplified representation of the variation with of the mass of visible matter enclosed inside .
The mass of visible matter in the galaxy is .
Show that for stars where the velocity of orbit is .
Draw on the axes the observed variation with r of the orbital speed v of stars in a galaxy.

Explain, using the equation in (a) and the graphs, why the presence of visible matter alone cannot account for the velocity of stars when .
Question 6
SLPaper 3The Hubble constant is accepted to be 70 km s Mpc. This value of the Hubble constant gives an age for the universe of 14.0 billion years. The accepted value of the Hubble constant has changed over the past decades.
The redshift of a galaxy is measured to be z = 0.19.
Explain how international collaboration has helped to refine this value.
Estimate, in , the distance between the galaxy and the Earth.
Determine, in years, the approximate age of the universe at the instant when the detected light from the distant galaxy was emitted.
Question 7
HLPaper 3The surface temperature of the star Epsilon Indi is .
Determine the peak wavelength of the radiation emitted by Epsilon Indi.
Using the axis, draw the variation with wavelength of the intensity of the radiation emitted by Epsilon Indi.

The following data are available for the Sun.
Surface temperature = 5800 K
Luminosity =
Mass =
Radius =
Epsilon Indi has a radius of 0.73 . Show that the luminosity of Epsilon Indiis 0.2 .
Epsilon Indi is a main sequence star. Show that the mass of Epsilon Indi is 0.64 .
The Sun will spend about nine billion years on the main sequence. Calculate how long Epsilon Indi will spend on the main sequence.
Describe the stages in the evolution of Epsilon Indi from the point when it leaves the main sequence until its final stable state.
Question 8
SLPaper 3The Hubble constant is s.
A galaxy is ly from Earth. Show that its recessional speed as measured from Earth is about m s.
A line in the hydrogen spectrum when measured on Earth has a wavelength of 486 nm. Calculate, in nm, the wavelength of the same hydrogen line when observed in the galaxy’s emission spectrum.
Outline how observations of spectra from distant galaxies provide evidence that the universe is expanding.
Question 9
SLPaper 3Distinguish between the solar system and a galaxy.
Distinguish between a planet and a comet.
Question 10
HLPaper 3The light from a distant galaxy shows that .
Calculate the ratio .
Outline how Hubble’s law is related to .
Hubble originally linked galactic redshift to a Doppler effect arising from galactic recession. Hubble’s law is now regarded as being due to cosmological redshift, not the Doppler effect. Explain the observed galactic redshift in cosmological terms.
