
Topic 2 - Mechanics
Question 1
SLPaper 1A motor of input power 160 W raises a mass of 8.0 kg vertically at a constant speed of 0.50 m s.
What is the efficiency of the system?
Question 2
SLPaper 2A student strikes a tennis ball that is initially at rest so that it leaves the racquet at a speed of 64 m/s. The ball has a mass of 0.058 kg and the contact between the ball and the racquet lasts for 25 ms.
The student strikes the tennis ball at point P. The tennis ball is initially directed at an angle of 7.00° to the horizontal.
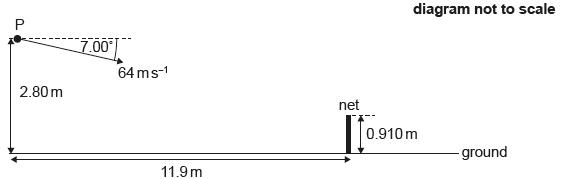
The following data are available:
- Height of P = 2.80 m
- Distance of student from net = 11.9 m
- Height of net = 0.910 m
- Initial speed of tennis ball = 64 m/s
Calculate the average force exerted by the racquet on the ball.
Calculate the time it takes the tennis ball to reach the net.
Calculate the average power delivered to the ball during the impact.
Show that the tennis ball passes over the net.
Determine the speed of the tennis ball as it strikes the ground.
Question 3
HLPaper 2A small metal pendulum bob is suspended at rest from a fixed point with a length of thread of negligible mass. Air resistance is negligible.
The pendulum begins to oscillate. Assume that the motion of the system is simple harmonic, and in one vertical plane.
The graph shows the variation of kinetic energy of the pendulum bob with time.
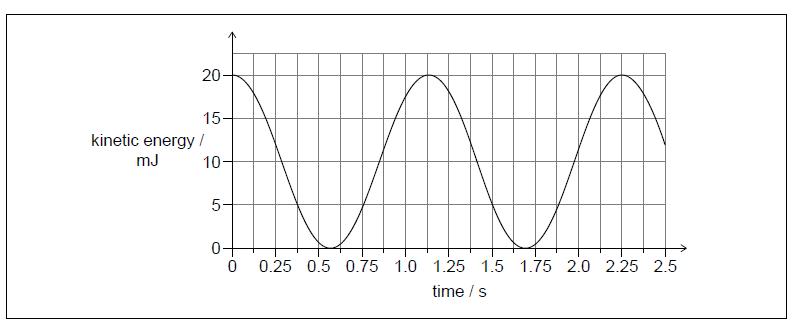
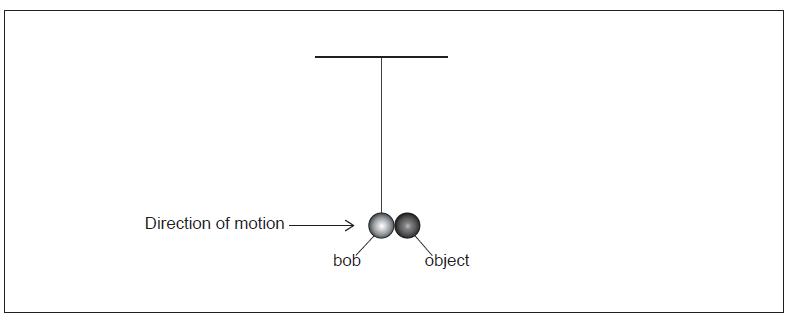
When the 75 g bob is moving horizontally at 0.80 m/s, it collides with a small stationary object also of mass 75 g. The object and the bob stick together.
Calculate, in m, the length of the thread. State your answer to an appropriate number of significant figures.
Label on the graph with the letter X a point where the speed of the pendulum is half that of its initial speed.
The mass of the pendulum bob is 75 g. Show that the maximum speed of the bob is about 0.7 m/s–1.
Calculate the speed of the combined masses immediately after the collision.
Show that the collision is inelastic.
Sketch, on the axes, a graph to show the variation of gravitational potential energy with time for the bob and the object after the collision. The data from the graph used in (a) is shown as a dashed line for reference.
The speed after the collision of the bob and the object was measured using a sensor. This sensor emits a sound of frequency and this sound is reflected from the moving bob. The sound is then detected by the sensor as frequency .
Explain why and are different.
Question 4
SLPaper 1An object is projected vertically upwards at time t = 0. Air resistance is negligible. The object passes the same point above its starting position at times 2s and 8s.
If g = 10 m s, what is the initial speed of the object?
Question 5
HLPaper 1A force acts on an object of mass 40 kg. The graph shows how the acceleration a of the object varies with its displacement d.
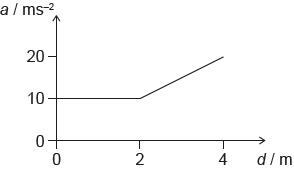
What is the work done by the force on the object?
Question 6
SLPaper 2A.small metal pendulum bob of mass 75 g is suspended at rest from a fixed point with a length of thread of negligible mass. Air resistance is negligible. The bob is then displaced to the left.
A. time the bob is moving horizontally to the right at 0.8 m/s. It collides with a small stationary object also of mass 75 g. Both objects then move together with motion that is simple harmonic.
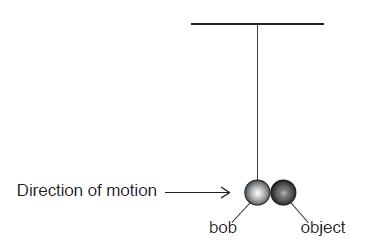
C.lculate the speed of the combined masses immediately after the collision.
Show that the collision is inelastic.
Describe the changes in gravitational potential energy of the oscillating system from as it oscillates through one cycle of its motion.
Question 7
SLPaper 1The mass at the end of a pendulum is made to move in a horizontal circle of radius at constant speed. The magnitude of the net force on the mass is .
 What is the direction of and the work done by during half a revolution?
What is the direction of and the work done by during half a revolution?
| Direction of | Work done by | |
|---|---|---|
| A. | towards centre of circle | zero |
| B. | towards centre of circle | |
| C. | away from centre of circle | zero |
| D. | away from centre of circle |
Question 8
SLPaper 1An electric motor of efficiency 0.75 is connected to a power supply with an emf of 20 V and negligible internal resistance. The power output of the motor is . What is the average current drawn from the power supply?
Question 9
SLPaper 1Question 10
HLPaper 2A metal sphere is charged positively and placed far away from other charged objects. The electric potential at a point on the surface of the sphere is 53.9 kV.
A small positively charged object moves towards the centre of the metal sphere. When the object is 2.8 m from the centre of the sphere, its speed is 3.1 m s. The mass of the object is 0.14 g and its charge is 2.4 × 10 C.
Outline what is meant by electric potential at a point.
The electric potential at a point a distance from the centre of the sphere is . Determine the radius of the sphere.
Comment on the angle at which the object meets equipotential surfaces aroundthe sphere.
Determine whether the object will reach the surface of the sphere.
Show that the kinetic energy of the object is about .
