

Figure 3 represents a system of aquaculture with four groups of harvestable species.
Figure 3: Integrated aquaculture
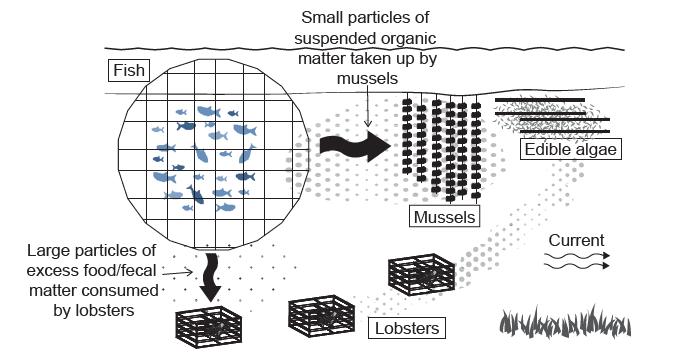
[Source: Adapted from and reprinted with permission from Ocean Conservancy]

Identify one producer in the system illustrated in Figure 3.

Outline one reason why aquaculture production has increased globally.

Describe two negative environmental impacts that may arise from integrated aquaculture.

Explain why this system may cause fewer environmental impacts than systems that farm only fish.

Describe two factors that influence the rate of infiltration in a drainage basin.

To what extent does the development of different societies impact their mitigation and adaptation strategies for climate change?

Outline how a positive feedback loop can impact an ecosystem.

Compare and contrast the impact of two named food production systems on climate change.

Describe the concept of a watershed and its importance in water resource management.

Describe two potential impacts of aquaculture on wild fish populations.

Discuss the environmental risks of overexploitation in marine ecosystems.

Describe two methods for improving the sustainability of aquaculture practices.

Analyze the following graph showing global aquaculture production over time:

Describe the trend shown in the graph.

Suggest two reasons for this trend.

Explain how feedback loops are involved in alternate stable states and the tipping points between them.

Earth’s atmospheric levels of carbon dioxide reached 400 ppm in 2016. Outline the potential impacts of high levels of greenhouse gases on human societies in different locations.

Discuss the consequences of changing global per capita meat consumption on the conservation of ecosystems and biodiversity.

Explain how soil can be viewed as an ecosystem.

Examine the role of humans in the destabilization of ecological systems.

Compare and contrast the impact of humans on the carbon and nitrogen cycles.
